Most women experience breast changes at some time. Your age, hormone levels, and medicines you take may cause lumps, bumps, and discharges (fluids that are not breast milk).
If you have a breast lump, pain, discharge or skin irritation, see your health care provider. Minor and serious breast problems have similar symptoms. Although many women fear cancer, most breast problems are not cancer.
Breast Abscess
A breast abscess is a collection of pus, resulting from an infection. Symptoms may include tenderness and inflammation. Antibiotics are prescribed to treat the infection, and your doctor may drain the pus.

Cysts
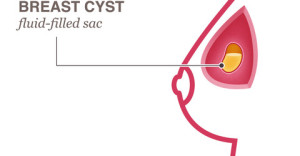
A cyst is a fluid-filled sac. The cause of breast cysts is unknown. In the vast majority of cases, cysts are not harmful, although they may cause pain. Cysts disappear sometimes by themselves, or your doctor may draw out the fluid with a needle.
Fibroadenomas
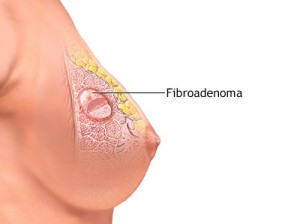
Fibroadenomas are fibrous, benign (noncancerous) growths in breast tissue. These growths are solid, usually painless lumps that are not attached to any structures in the breast. A fibroadenoma is usually removed surgically, using a local anesthetic.
Fibrocystic Breast Disorders
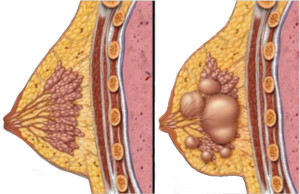
Fibrocystic breast disease is a common condition characterized by an increase in the fibrous and glandular tissues in the breasts, which results in small, nodular cysts, noncancerous lumpiness, and tenderness. Although called a “disease,” this condition is not a disease. There is no specific treatment for fibrocystic disease. Treatment of the cysts may be all that is needed (see Cysts above).
Tumours
A tumor that is precancerous or cancerous usually shows up as a white area on a mammogram even before it can be felt. In cases where the tumor is cancerous, it may appear as a white area with radiating arms. A cancerous tumor may have no symptoms or may cause swelling, tenderness, discharge from the nipple or indentation of the nipple, or a dimpled appearance in the skin over the tumor (see inset). A breast biopsy is helpful in determining whether a mass is cancerous.


 Mammogram
Mammogram MRI
MRI Ultrasound
Ultrasound